The difference of Global Business Culture
Communication
The American’s communication is very straight. Therefore, it is easy to understand what they are thinking. On the other hand, the Japanese are really shy, so it isn’t easy to understand.
Humanity
Salary
Time
How to sell the product globally as a first step
Selling the product to a place you’ve never tried is difficult for each corporation. Because of the lack of knowledge, it is harder to calculate estimates.
Major Ways
B2C: Amazon
When this is the first time for selling, I recommend Amazon because there is a lack of lots. Sure! Here’s a concise text summarizing the key points for selling on Amazon as a seller:
Selling on Amazon offers a great opportunity to reach a global audience and grow your business. Start by creating an Amazon seller account and listing your products with detailed descriptions and images. You can choose between Fulfillment by Amazon (FBA), where Amazon handles storage, packing, and shipping, or Fulfilled by Merchant (FBM), where you manage these tasks yourself.
Utilize Amazon’s advertising tools like Sponsored Products to increase visibility. If you have a registered trademark, enroll in Amazon Brand Registry for additional brand protection and enhanced content options. Providing excellent customer service is crucial for maintaining high seller ratings. Use Amazon’s analytics tools to track performance and make informed decisions.
Consider expanding your reach by selling on Amazon’s international marketplaces through the Amazon Global Selling program. This allows you to navigate international sales with tools for currency conversion and shipping.
By leveraging these features, you can effectively manage and grow your business on Amazon.

B2B: Alibaba
When you would like to make a lot of money, SASAL recommends Alibaba for B2B sales. Alibaba provides access to a vast global marketplace, connecting sellers with millions of potential buyers worldwide. Sellers benefit from competitive pricing due to direct access to manufacturers, which can significantly reduce costs. The platform supports bulk purchasing, allowing for higher profit margins. Additionally, Alibaba offers various tools for secure transactions, including Trade Assurance and verified suppliers, ensuring reliability and buyer protection. Sellers can also customize products and packaging, enhancing brand identity. Overall, Alibaba’s extensive reach, cost-effectiveness, and secure environment make it an ideal platform for expanding your business globally.

Google Advertismenent
If you are able to sell the product continually, SASAL recommends advertisement via Google ads to expand the brand image to the target segment. Google Ads provides access to a vast audience, as Google is the world’s largest search engine, handling billions of searches each month1. This platform allows sellers to target specific keywords, ensuring their ads reach potential customers with high purchase intent. The advanced targeting capabilities include demographics, locations, and interests, helping to reach the right audience at the right time. Google Ads also offers fast results, with ads appearing almost immediately after campaign launch. Additionally, the platform provides robust tracking and reporting tools, enabling data-driven optimizations to maximize ROI. Overall, Google Ads is a powerful tool for increasing visibility, driving traffic, and boosting sales.

LinkedIn Advertisement
When you would like to appear the product to a particular segment, it’s better for us to make use of LinkedIn ads. LinkedIn Ads provide access to a highly targeted professional audience, making it ideal for B2B marketing. The platform allows precise targeting based on job titles, industries, and company sizes, ensuring your ads reach decision-makers with significant buying power1. LinkedIn users are often engaged and ready to interact with professional content, leading to higher conversion rates1. Additionally, LinkedIn Ads offer various formats, including Sponsored Content, Sponsored Messaging, and Dynamic Ads, allowing for versatile and impactful campaigns1. Overall, LinkedIn Ads help increase brand visibility, generate quality leads, and drive meaningful engagement.

SASAL Supports
Another way the advertisement is written on this page is that SASAL is able to support the advertisement phase.
Other Articles
Who publish the world data as a government organization?
What kinds of search engine in the world
What is the Sector?
How to maximize your corporation’s advertisement
Advertising is a crucial aspect of any business strategy, and there are numerous ways to reach potential customers. Each method has its unique strengths and can be tailored to fit specific goals and audiences. Based on your intent we need to change the way of the advertisement. Also, talking about the advertisement, it is better for each corporation to do it themselves because it takes a lot of knowledge of your corporation and costs, even if you ask the advertisement to the others it tends to be no mean unfortunately. In this article, SASAL shares the basic knowledge of the advertisement.
Traditional Advertising
Print Advertising remains a powerful tool, especially for local businesses. For instance, a local restaurant might place a full-page ad in the Sunday newspaper to attract weekend diners. Magazines offer a way to target niche audiences; a high-end watch brand might advertise in a luxury lifestyle magazine to reach affluent readers. Brochures and flyers are versatile and cost-effective, perfect for promoting local events or new business openings.
Broadcast Advertising includes television and radio commercials. TV ads are particularly impactful due to their visual and auditory storytelling capabilities. For example, Coca-Cola’s holiday commercials often feature heartwarming stories that resonate with viewers. Radio ads, on the other hand, can target specific demographics based on the station and time slot. A local car dealership might run ads during morning commutes to reach potential buyers.
Outdoor Advertising is another traditional method that remains effective. Billboards in high-traffic areas are hard to miss and great for brand recall. A tech company might use billboards in Silicon Valley to promote a new gadget. Transit ads, such as those on buses and trains, are effective in urban areas with heavy public transportation use. A movie studio might advertise a new film on subway cars to reach daily commuters.
Direct Mail involves sending personalized promotional materials directly to consumers. This method can be highly targeted and engaging. For example, a real estate agent might send postcards to homeowners in a specific area, highlighting recent sales and offering free home valuations.
Digital Advertising
Social Media Advertising has revolutionized the way businesses reach their audiences. Platforms like Facebook and Instagram allow for precise targeting based on user data. A fashion brand might use Instagram ads to showcase new collections to users who have shown interest in similar brands. LinkedIn is ideal for B2B marketing, where a software company might use ads to reach decision-makers in specific industries.
Search Engine Advertising includes Pay-Per-Click (PPC) and Search Engine Optimization (SEO). PPC ads appear in search engine results, and advertisers pay only when the ad is clicked. An online retailer might bid on keywords like “buy running shoes” to appear at the top of search results. SEO involves improving website content to rank higher organically. A travel blog might optimize articles for keywords like “best travel destinations 2024” to attract more visitors.
Display Advertising involves banner ads on websites, which can be targeted based on user behavior. An electronics retailer might display ads for laptops on tech news sites. Video Advertising, such as pre-roll ads on YouTube, is engaging and can convey complex messages effectively. A car manufacturer might run a 30-second ad showcasing a new model before a popular tech review video.
Native Advertising blends in with the platform’s content, making it less intrusive and more engaging. A financial services company might publish a sponsored article on a news website about retirement planning.
Other Methods
Content Marketing focuses on creating valuable content to attract and engage an audience. A skincare brand might run a blog with tips on skincare routines, subtly promoting their products. Influencer Marketing involves partnering with influencers to promote products. A fitness brand might collaborate with a popular fitness influencer to showcase their new workout gear on Instagram.
Email Marketing is a direct way to reach customers. An e-commerce site might send a weekly newsletter with special offers and new arrivals. Mobile Advertising includes ads designed for mobile devices, such as in-app ads. A game developer might run ads for their new game within other popular mobile games.
Guerilla Marketing uses unconventional strategies to grab attention. A beverage company might set up a flash mob in a busy city square to promote a new drink.
Examples of Effective Advertising Techniques
Storytelling is a powerful tool in advertising. Nike’s “Just Do It” campaign often features stories of athletes overcoming challenges, which resonates deeply with viewers. Color Psychology uses colors to evoke emotions. McDonald’s uses red and yellow to stimulate appetite and create a sense of urgency.
FOMO (Fear of Missing Out) creates urgency. Limited-time offers like Amazon’s Prime Day create a rush to buy before the deals end. Social Proof leverages testimonials and reviews. Amazon prominently displays customer reviews and ratings to build trust and encourage purchases. Influencer Advertising uses influencers’ reach. A beauty brand might partner with a YouTube makeup artist to demonstrate their products in tutorials.
By understanding and utilizing these advertising methods, businesses can effectively reach and engage their target audience. Each method can be tailored to fit specific goals, ensuring a successful advertising strategy.
SASAL Support
SASAL, INC is focused on Digital Advertising. If you would like to insource Digital Advertising, please feel free to contact us. SASAL recommends the maximum advertisement for your corporation with optimization. Thank you.
Other Articles
Who publish the world data as a government organization?
What kinds of search engine in the world
What is the Sector?
How to monetize the YouTube within one month
The background of YouTube is amazing, as we expected. If you have a corporation, SASAL strongly recommends that you have your own advertisement platform, like YouTube. In this article, SASAL recommends how to monetize YouTube within one month.
Contents Direction
For the right operation of YouTube, we need to consider the right content.
Famous Contents
Normal Contents
Core Contents
Monetization
For Register: Google Ad
By using the
For watching hour: YouTube
Other Articles
Who publish the world data as a government organization?
What kinds of search engine in the world
What is the Sector?
How to make use of the Amazon for logistics.
SASAL is using the logistics department as an advertisement.
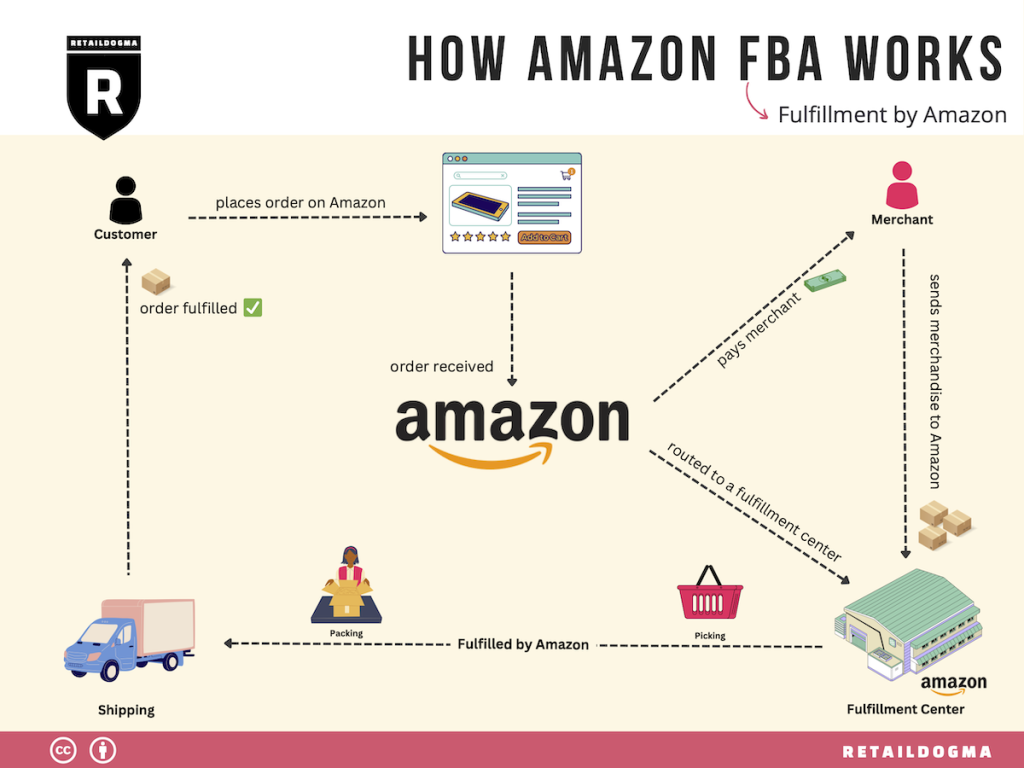
Other Articles
Who publish the world data as a government organization?
What kinds of search engine in the world
What is the Sector?
Trademark Registration
Check the trademark registration in the world tool.
https://www.wipo.int/web/global-brand-database
SASAL, INC. could not register a Trademark as a subcontractor corporation because there is no authorized staff. However, we can help you by using our knowledge of past trademark registration.
1. Determine Eligibility
- Distinctiveness: Your mark must be distinctive and not merely descriptive of the goods or services.
- Non-conflicting: It should not be confusingly similar to existing trademarks.
2. Conduct a Trademark Search
- USPTO’s TESS: Use the Trademark Electronic Search System (TESS) to check for existing trademarks that might conflict with yours.
- Professional Search: Consider hiring a trademark attorney to conduct a thorough search.
3. Create a USPTO Account
- USPTO Website: Register for an account on the USPTO website to access the Trademark Electronic Application System (TEAS).
4. Complete the Application
- Details Required: Provide information about your mark, the goods or services it will represent, and your basis for filing (use in commerce or intent to use).
- Specimen: Submit a specimen showing how the mark is used in commerce (e.g., labels, tags, or packaging).
5. Submit and Pay
- TEAS: File your application online through TEAS.
- Fees: Pay the required filing fee, which varies depending on the type of application and number of classes of goods/services.
6. Examination by USPTO
- Initial Review: An examining attorney will review your application to ensure it meets all legal requirements.
- Office Actions: You may receive an office action requiring additional information or clarification. Respond promptly to avoid delays.
7. Publication and Opposition
- Official Gazette: If your application passes the initial review, it will be published in the USPTO’s Official Gazette.
- Opposition Period: Third parties have 30 days to file an opposition if they believe your mark will harm their business.
8. Registration
- No Opposition: If there are no oppositions or if you successfully overcome them, your trademark will be registered.
- Certificate: You will receive a certificate of registration from the USPTO.
9. Post-Registration Maintenance
- Continued Use: You must continue to use your trademark in commerce.
- Renewal: File maintenance documents and pay fees at regular intervals to keep your registration active.
10. Check Status
When you would like to search the status of the Trademark, you could from here.
For more detailed guidance, you can visit the USPTO website123.
Madrid e-Filing is a web service provided by the World Intellectual Property Organisation (WIPO).
Madrid e-Filing allows you to file an online application for international registration of your trade mark with the home Office and pay the fees. Madrid e-Filing also allows you to correct any deficiencies in your application and to respond to WIPO’s notification of deficiencies.
Certainly! Here are the detailed steps and features of the Madrid Protocol for international trademark registration:
Overview of the Madrid Protocol
The Madrid Protocol, officially known as the Protocol Relating to the Madrid Agreement Concerning the International Registration of Marks, is an international treaty that simplifies the process of registering trademarks in multiple countries. It was adopted in 1989 and came into force in 199612.
Key Features
- Single Application: You can file one application, in one language, and pay one set of fees to seek protection in multiple member countries2.
- WIPO Administration: The World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO) administers the Madrid System, which includes both the Madrid Agreement and the Madrid Protocol1.
- Languages: Applications can be submitted in English, French, or Spanish2.
- Cost-Effective: It is generally more cost-effective than filing separate applications in each country2.
- Centralized Management: You can manage your international trademark portfolio through a single, centralized system, including renewals and changes2.
Steps to Register a Trademark under the Madrid Protocol
- Basic Application: Start with a national or regional trademark application or registration in your home country (known as the “basic application” or “basic registration”).
- International Application: File an international application through your national or regional trademark office, which will forward it to WIPO.
- Examination by WIPO: WIPO examines the application for formalities and, if everything is in order, records the mark in the International Register and publishes it in the WIPO Gazette of International Marks.
- Notification to Designated Countries: WIPO notifies the trademark offices of the countries where you seek protection.
- National Examination: Each designated country examines the application according to its own laws. If a country raises no objections within a specified period (usually 12-18 months), the mark is protected in that country.
- Opposition Period: There may be an opposition period during which third parties can oppose the registration in some countries123.
Benefits
- Simplified Process: Streamlines the process of obtaining trademark protection in multiple countries.
- Cost Savings: Reduces the costs associated with filing separate applications in each country.
- Efficient Management: Allows for easy management of renewals and changes to the trademark registration through a single system2.
Post-Registration
- Maintenance: You must maintain the trademark by using it in commerce and renewing it periodically.
- Changes and Renewals: Any changes to the trademark registration, such as changes in ownership or address, can be made centrally through WIPO2.
The Madrid Protocol is a powerful tool for businesses looking to protect their trademarks internationally in a streamlined and cost-effective manner123.
Shop Story
SASAL, INC. sells products to clients. We are doing this one at retail cost, and other products are said to be three times the cost. SASAL sells its products at two times the price to ensure SASAL’s clients can utilize the excellent service for a long time(the cost price includes a shipping fee). Please ask a counselor when you want to ask about the product based on your corporation’s strategy. SASAL, INC. adds the products by hearing your opinion.

How to trade from the Manufacturer
SASAL, INC. operates this service for corporations that lack internal knowledge or internal operations. Because of the client, it is cheaper than other SASALs to use Alibaba.com to import the product. Those are the flow of SASAL, INC. It takes two months at most. When you would like to shorten and lower the costs of operating your corporation, that will be realized.
- SASAL, INC got the payment from the client.
- SASAL, INC orders the product to the vendor.
- SASAL, INC got the product from the vendor.
- SASAL, INC ships the product to the client.
- The client gets the products.
How to check the cost in general
- On the mobile phone, please open the Amazon.
- Scan the picture on camera.
- You could see the cost in general.
Other Articles
Who publish the world data as a government organization?
What kinds of search engine in the world
What is the Sector?
Important things corps need considering before a global trade
In this article, SASAL would like to share the importance of global trade. Tariffs are a powerful tool in international trade policy, used to protect domestic industries, generate revenue, and influence trade relationships. However, they can also lead to higher consumer prices and trade disputes. Understanding how tariffs work helps in comprehending the complexities of global trade dynamics.
United States
The United States remains a pivotal player in global trade, characterized by its substantial import and export activities. Here are some detailed trends:
- Reshoring Manufacturing: In recent years, there has been a significant push to bring manufacturing back to the U.S. This initiative aims to reduce dependency on foreign supplies, particularly in critical sectors such as technology and pharmaceuticals. The COVID-19 pandemic highlighted vulnerabilities in global supply chains, prompting this shift.
- Trade Deficit: The U.S. often runs a trade deficit, meaning it imports more than it exports. This is particularly evident in consumer goods and electronics. Efforts to balance this deficit include negotiating new trade deals and imposing tariffs on certain imports.
- Technological Exports: Despite the trade deficit, the U.S. is a leading exporter of advanced technology products, including aerospace, medical devices, and software.
China
China continues to dominate global trade with its vast export of manufactured goods. Detailed trends include:
- High-Tech Imports: To support its manufacturing sector, China has been increasing its imports of high-tech products and raw materials. This includes semiconductors, which are crucial for electronics manufacturing.
- Belt and Road Initiative: This ambitious infrastructure project aims to expand trade routes and partnerships across Asia, Africa, and Europe. By investing in infrastructure in these regions, China is creating new markets for its goods and securing supply chains.
- Export Dominance: China remains the world’s largest exporter, with significant exports in electronics, machinery, and textiles. The country’s trade policies and competitive pricing have solidified its position in global markets.
Germany
Germany’s economy is heavily reliant on exports, particularly in the automotive and machinery sectors. Here are some detailed insights:
- Export Reliance: A significant portion of Germany’s GDP comes from exports. This makes the country highly sensitive to global economic shifts and trade policies. For instance, trade tensions between major economies can have a direct impact on German exports.
- Trade Surplus: Germany often runs a trade surplus, meaning it exports more than it imports. This surplus is driven by high demand for German engineering and manufacturing, particularly in the automotive sector.
- Green Technology: Germany is also a leader in green technology exports, including renewable energy solutions and energy-efficient machinery. This aligns with global trends towards sustainability and environmental responsibility.
India
India is expanding its trade footprint by diversifying its export base. Detailed trends include:
- Pharmaceuticals and Electronics: India is becoming a major exporter of pharmaceuticals and electronics. The country’s pharmaceutical industry is known for producing generic drugs at competitive prices, while its electronics sector is growing rapidly.
- Trade Agreements: India is actively seeking new trade agreements to boost exports and reduce trade barriers. These agreements aim to open up new markets for Indian goods and services, enhancing the country’s global trade presence.
- Service Exports: In addition to goods, India is a leading exporter of IT services. The country’s IT sector provides software development, customer support, and other services to clients around the world.
Japan
Japan’s trade is characterized by high-tech exports and a significant trade surplus. Detailed trends include:
- Technological Exports: Japan is known for its advanced technology products, including automobiles, electronics, and robotics. These high-value exports contribute significantly to the country’s trade surplus.
- Supply Chain Challenges: Japan faces challenges from regional competition and shifting global supply chains. The country is adapting by investing in new technologies and seeking to diversify its supply sources.
- Aging Population: Japan’s aging population presents both challenges and opportunities for trade. While it may reduce the domestic labor force, it also drives demand for advanced healthcare technologies and services.
Developing Countries
Many developing countries are working to increase their participation in global trade. Detailed trends include:
- Infrastructure Improvements: Investing in infrastructure is a key strategy for many developing countries. Improved ports, roads, and communication networks facilitate trade and attract foreign investment.
- Reducing Barriers: Efforts to lower trade barriers, such as tariffs and quotas, are helping developing countries integrate more fully into the global economy. These measures make it easier for these countries to export their goods and services.
- Diversification: Developing countries are diversifying their economies to reduce reliance on a single export commodity. This includes expanding into new sectors such as manufacturing, services, and technology.
What Are Tariffs?
Tariffs are taxes or duties imposed by a government on imported goods. They are designed to make imported products more expensive compared to domestic products, thereby protecting local industries from foreign competition1.
- Ad Valorem Tariffs: These are calculated as a percentage of the value of the imported goods. For example, a 10% ad valorem tariff on a $100 item would add $10 to its cost2.
- Specific Tariffs: These are fixed fees based on the quantity of goods imported, such as $5 per kilogram2.
- Compound Tariffs: These combine both ad valorem and specific tariffs, applying a percentage of the value plus a fixed fee2.
How Tariffs Work
- Imposition: When a country imposes a tariff, it increases the cost of imported goods. This makes foreign products less competitive compared to domestic products2.
- Collection: Tariffs are collected by the customs authority of the importing country. For example, in the U.S., the Customs and Border Protection agency collects tariffs on behalf of the Commerce Department2.
- Impact on Prices: The additional cost of tariffs is usually passed on to consumers, leading to higher prices for imported goods2.
Reasons for Tariffs
- Protecting Domestic Industries: Tariffs protect emerging or struggling domestic industries from foreign competition by making imported goods more expensive2.
- Revenue Generation: Governments use tariffs as a source of revenue2.
- Retaliation: Tariffs can be used as a tool for retaliation in trade disputes. If one country imposes tariffs, the affected country might respond with its own tariffs3.
- National Security: Tariffs can protect industries crucial to national security, such as defense and technology2.
Effects of Tariffs
- Trade Flows: Tariffs can alter global trade flows by making certain goods more expensive and less attractive to import3.
- Economic Impact: While tariffs can protect domestic jobs and industries, they can also lead to higher prices for consumers and potential trade wars3.
- Retaliation: Countries affected by tariffs often impose retaliatory tariffs, which can escalate into trade disputes and reduce overall trade3.
Examples of Tariffs in Action
- U.S.-China Trade War: The U.S. imposed tariffs on Chinese goods to address trade imbalances and intellectual property theft. China responded with its own tariffs on U.S. goods, leading to a significant reduction in trade between the two countries3.
- EU Tariffs on Steel: The European Union has imposed tariffs on steel imports to protect its steel industry from cheaper foreign steel, particularly from China2.
1: MasterClass 2: Investopedia 3: The Hartford
SASAL, INC is able to support global trade for both sides, including supplier buyers. Please join the SASAL Counselor first.
Other Articles
Who publish the world data as a government organization?
What kinds of search engine in the world
What is the Sector?
How Many Languages Are There in the World?
Language History
Early humans likely used gestures and sounds to communicate as a Prehistoric Communication. Spoken language is believed to have developed around 100,000 to 200,000 years ago. These are hypothetical, reconstructed languages that are the ancestors of modern languages. Proto-Indo-European is one of the most studied proto-languages. As ancient languages, Sumerians and Egyptians used some of the earliest written languages, dating back to around 3000 BCE. Sumerian cuneiform and Egyptian hieroglyphs are among the first writing systems. Classical Languages Greek and Latin played significant roles in developing Western languages. Sanskrit was crucial in South Asia. As Ancient Languages, Sumerian and Egyptian are some of the earliest written languages, dating back to around 3000 BCE. Sumerian cuneiform and Egyptian hieroglyphs are among the first writing systems. Greek and Latin, as classical languages, played significant roles in developing Western languages. Sanskrit was crucial in South Asia. As Medieval to Modern Languages, Middle Ages: Languages like Old English, Old French, and Old High German evolved. The Norman Conquest of England in 1066 significantly influenced the English language. Renaissance and Beyond: The invention of the printing press in the 15th century helped standardize languages. Modern languages like English, Spanish, French, and others began to take their current forms. As Contemporary Languages, Globalization: Today, languages continue to evolve. English has become a global lingua franca, while millions worldwide speak other languages like Mandarin Chinese, Spanish, and Hindi. Digital Age: The internet and technology have introduced new words and phrases, influencing how languages are used and developed.
Languages by Region
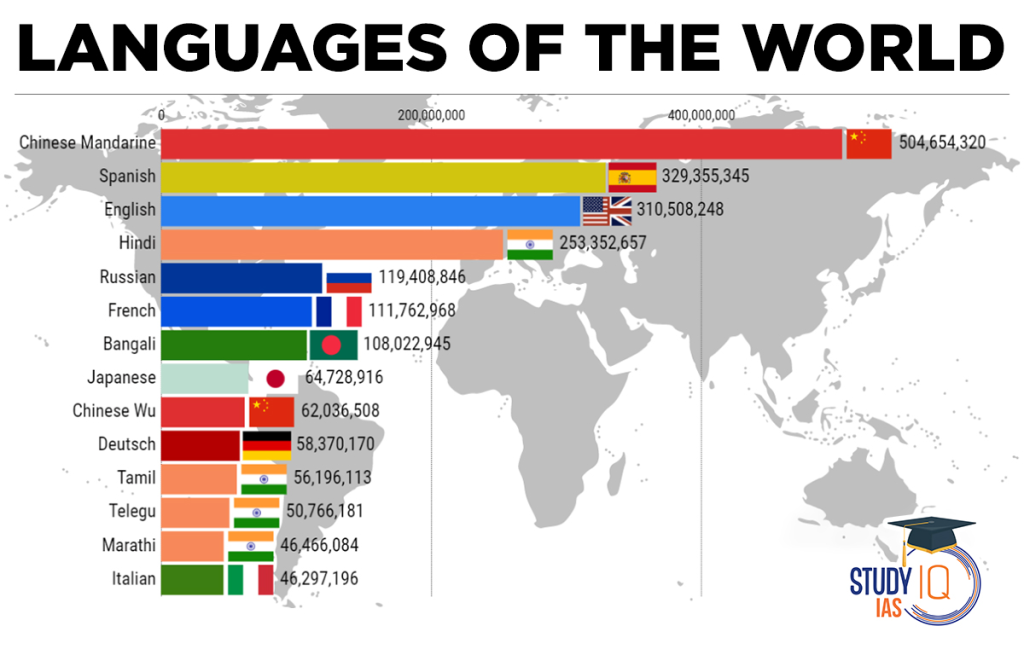
Asian Provinces
| East Asia | Japanese, Korean, Chinese (Continental Simplified Chinese, Hong Kong Taiwan Traditional Chinese) Mongolian (Hong Kong-Taiwanese Traditional Chinese) |
| Southeast Asia | Thai, Burmese, Malay, Indonesian |
| Central Asia | Uzbek, Kazakh, Kyrgyz, Tajik, Turkmen |
| South Asia | Hindi, Bengali, Sinhala, Tamil, Nepali, Urdu, Dzongkha, Dibech, Dari, Pashto |
| West Asia | Arabic, Turkish, Georgian, Persian, Kurdish, Hebrew |
European Province
| Eastern Europe | Russian, Belarusian, Ukrainian, Czech, Slovak, Hungarian, Croatian, Romanian, Armenian |
| Northern Europe | Greenlandic, Icelandic, Norwegian, Swedish, Finnish Finnish, Lithuanian, Latvian, Estonian, Danish. |
| Western Europe | English (British), German, French, Dutch, Romansh |
| Southern Europe | Spanish, Portuguese, Catalunya, Italian, Lat, Maltese, Slovenian, Croatian, Bosnian, Serbian, Albanian, Greek, Bulgarian, Montenegrin, Macedonian |
American States
| North America | English (American style), French (Canadian). |
| Central America | English (US style), Spanish. |
| Caribbean | English (US style), Spanish, French, Portuguese, Creole |
| South America | English (US style), Spanish (South America), Portuguese (Brazil), Guarani |
Oceania
| Australia and New Zealand | English (British), Maori |
| Melanesia, Polynesia, Micronesia | English (British), French, Chamorro, Palauan, Kiribati, Samoan, Tuvaluan, Tongan, Nauru, Niue, Bislama, Fijian, Hindustani, Tahitian, Marshallese |
African Provinces
| North Africa | Berber, Arabic. |
| West Africa | Arabic, French, English (British), Cape Verdean |
| Central Africa | Arabic, French, English (British), Sango, Spanish, Portuguese |
| East Africa | Arabic, Tigrinya, Amharic, Swahili, English, Somali, Portuguese, Madagascar, Comorian, French, Creole, Lundi, Rwandan |
| South Africa | English (British), Tswana, Afrikaans, Sotho, Swazi |
List of Official Languages by Country
| Country Name | Official language |
|---|---|
| Icelandic | Icelandic |
| Irish | Irish, English |
| Azerbaijani | Azerbaijani |
| Afghanistan | Dari, Pashto |
| American (American style) | English (American Style) |
| United Arab Emirates | Arabic |
| Algeria | Arabic |
| Argentine | Spanish |
| Alba | Dutch, Papiamento |
| Albania | Albanian |
| Armenian | Armenian Language |
| Anguilla | English (American Style) |
| Angolan | Portuguese |
| Antigua and Barbuda | English (American Style) |
| Andorra | Catalan |
| Yemeni | Arabic (British) |
| United Kingdom | English (British) |
| Israel | Hebrew, Arabic |
| Italian | Italian |
| Iraqi | Arabic, Kurdish |
| Iran | Persian, Turkish, Kurdish |
| India | Hindi, English (British), Assamese, Bengali, Bodo, Daughtry, Gujarati, Kannada, Kashmiri, Konkani, Maithili, Malayalam, Manipuri, Marathi, Nepali, Oriya, Punjabi, Sanskrit, SanthalSindhi, Tamil, Telugu, Urdu |
| Indonesia | Indonesian |
| Uganda | English (British), Swahili |
| Ukraine | Ukrainian |
| Uzbekistan | Uzbek |
| Uruguayan | Spanish |
| Ecuador | Spanish |
| Egyptian | Arabic |
| Estonian | Estonian Language |
| Estwatini (Estonian) | English (British), Swazi |
| Ethiopian | Amharic |
| Eritrean | Arabic, Tigrinya |
| El Salvador | Spanish |
| Australian | English (British) |
| Austrian | German |
| Omani | Arabic |
| Dutch | Dutch |
| Ghanaian | English (British Style) |
| Cape Verdean | Cape Verdean, Portuguese |
| Guyana | English (British Style) |
| Kazakhstan | Kazakh, Russian |
| Qatar | Arabic |
| Canadian | English (American Style), French |
| Gabon | French |
| Cameroon | English (British), French |
| Gambia | English (British style) |
| Cambodia | Khmer (Cambodian) |
| Guinea (Guinea) | French language |
| Guinea-Bissau | Portuguese |
| Cyprus | Modern Greek, Turkish |
| Cuban | Spanish |
| Greek | Greek (language) |
| Kiribati | Kiribati, English (American Style) |
| Kyrgyz | Kyrgyz, Russian |
| Guatemala | Spanish |
| Guam | English (American Style), Chamorro |
| Kuwaiti | Arabic |
| Cook Islands | Cook Islands Maori, English (American Style) |
| Greenland | Greenlandic |
| Grenada | English (American Style) |
| Croatian | Croatian, Italian |
| Cayman Islands | English (U.S. style) |
| Kenya | Swahili, English (British) |
| Cote d’Ivoire | French |
| Costa Rica | Spanish |
| Comoros | Arabic, Comorian, French |
| Colombian | Spanish |
| Republic of the Congo | French language |
| Democratic Republic of the Congo | French |
| Saudi Arabia | Arabic |
| Samoa | Samoan, English (American Style) |
| Sao Tome and Principe | Portuguese |
| Zambia | English (British Style) |
| Saint Pierre and Miquelon | French Language |
| San Marino | Italian |
| Sierra Leone | English (British style) |
| Djibouti | Arabic, French |
| Gibraltar | English (British Style) |
| Jamaican | English (American Style) |
| Georgian (Georgia) | Georgian (Georgia) |
| Syriac | Arabic |
| Singapore | Malay, English (British), Chinese (Hong Kong-Taiwanese masculine and simplified Mainland Chinese), Tamil |
| Zimbabwe | English (British style) |
| Swiss | German, French, Italian, Romansh |
| Swedish | Swedish |
| Sudanese | Arabic, English (British) |
| Spanish (English) | Spanish in Spain |
| Suriname | Dutch |
| Sri Lanka | Sinhala, Tamil |
| Slovak | Slovak |
| Slovenian | Slovenian |
| Seychelles | Creole, English (British), French |
| Senegalese | French |
| Serbia | Serbian |
| St. Kitts and Nevis | English (U.S. style) |
| Saint Vincent and the Grenadines | English (American Style) |
| Saint Lucia | English (American Style) |
| Somalia | Somali, Arabic |
| Solomon Islands | English (British) |
| Thai (Thai) | Thailand |
| Tajikistan | Tajik |
| Tanzania | Swahili, English (British) |
| Czech | Czech language |
| Chad | Arabic, French |
| Tunisia | Arabic |
| Chile | Spanish |
| Tuvalu | Tuvaluan, English (British) |
| Danish | Danish |
| German | German |
| Togo | French |
| Dominica | English (American Style) |
| Dominican Republic | Spanish (Spain) |
| Trinidad and Tobago | English (American Style) |
| Turkmenistan | Turkmen Language |
| Turkey | Turkish |
| Tongan | Tongan, English (British) |
| Nigeria | English (British Style) |
| Nauru | English (British), Nauruan |
| Namibia | English (British) |
| Niue | Niue, English (British) |
| Nicaragua | Spanish, English (American Style) |
| Niger | French Language |
| New Caledonia | French Language |
| New Zealand | English (British), Maori, New Zealand Sign Language |
| Nepalese | Nepalese |
| Norwegian | Norwegian |
| Bahraini | Arabic |
| Haitian | French, Creole |
| Pakistani | Urdu, English (British) |
| Vatican | Latin |
| Panama | Spanish |
| Vanuatu | French, English (British), Bislama |
| Bahamas | English (American Style) |
| Papua New Guinea | English (British), Tok Pisin.Hrimotsu |
| Bermuda Islands | English (U.S. style), Portuguese |
| Palau | Palauan, English (British) |
| Palaguay | Spanish, Guarani |
| Barbados | English (American Style) |
| Hungarian | Hungarian |
| Bangladeshi | Bengali |
| Fiji | English (British), Fijian, Hindustani |
| Philippines | Tagalog, English (American Style) |
| Finland | Finnish, Swedish |
| Bhutanese | Dzongkha |
| Puerto Rico | Spanish, English (U.S. style) |
| Brazil | Portuguese |
| French | French Language |
| French Guiana | French Guiana |
| French Polynesia | French, Tahitian |
| Bulgaria | Bulgaria |
| Burkina Faso | French |
| Brunei | Malay, English (British) |
| Burundi | Swahili, French, Lundi |
| Vietnamese | Vietnamese |
| Benin | French Language |
| Venezuela | Spanish |
| Belarus | Belarusian, Russian |
| Belize | English (U.S. style), Spanish |
| Peruvian | Spanish |
| Belgian | Dutch, French, German |
| Polish | Polish |
| Bosnia and Herzegovina | Croatian, Serbian, Bosnian |
| Botswana | English (British), Tswana |
| Bolivia | Spanish |
| Portuguese, Miranda | Portuguese, Miranda |
| Honduras | Spanish |
| Marshall Islands | Marshallese, English (American Style) |
| Macau | Portuguese, Chinese (Hong Kong Taiwanese Traditional) |
| Madagascar | Malagasy, French |
| Malawi | English (British) |
| Mali | French |
| Malta | Maltese, English (British) |
| Malaysia | Malay, Chinese (Hong Kong-Taiwanese masculine and simplified Mainland Chinese), Tamil, English (British) |
| Micronesia, Federated States of | English (American Style) |
| Myanmar (Burmese) | Burmese (Myanmar) |
| Mexican (Mexico) | Spanish |
| Mauritius | English (British), French, Creole |
| Mauritania | Arabia |
| Mozambique | Portuguese |
| Monaco | French Language |
| Maldives | Dibehi |
| Moldovan | Ukrainian, Gagauz, Moldovan, Russian |
| Morocco | Arabic, Berber, French |
| Mongolian | Mongolian |
| Montenegro | Montenegrin, Serbian |
| Jordanian | Arabic |
| Lao | Lao |
| Latvian | Latvian Language |
| Lithuanian | Lithuanian Language |
| Libyan | Arabic |
| Liechtenstein | German |
| Liberia | English (British style) |
| Romanian (Romanian) | Romanian |
| Luxembourgish | French, German, Luxembourgish |
| Rwanda | Rwandan, French, English (British) |
| Lesotho | English (British), Sotho |
| Lebanese | Arabic |
| Reunion | French |
| Russian | Russian |
| Korean | Korean |
| Hong Kong | English (British), Chinese (Traditional Hong Kong-Taiwanese) |
| Equatorial Guinea | Spanish, French, Portuguese |
| Taiwanese | Chinese (Hong Kong Taiwanese Traditional) |
| Central Africa | French, Coral |
| Chinese (simplified continental style) | Chinese (Simplified Mainland Style) |
| East Timor | Tetum, Portuguese |
| South Africa | Afrikaans, English (British), Zulu, Ndebele, Northern Sotho, Sotho, Swazi, Tsonga, Tswana, Venda, Kosa |
| Japanese | Japanese |
| American Samoa | English (American Style), Samoan |
| North Macedonia | Albanian, Serbian, Turkish, Macedonian, Roma |
| Northern Mariana Islands | English (U.S. style), Chamorro, Carolinian |
| North Korean | Korean |
SASAL Case
SASAL shows our companies’ language level. Please refer to this.
English
Japanese
Spanish
French
