Each type of investment corporation plays a unique role in the financial ecosystem, catering to different stages of company growth and investment strategies. Investment banks facilitate capital raising and provide advisory services, private equity firms focus on mature companies needing restructuring, venture capital firms invest in high-growth startups, and corporate venture capital entities seek strategic synergies with innovative startups. Understanding these differences can help investors and entrepreneurs navigate the complex world of finance more effectively.
Understanding the distinction between investment and financing is crucial for effective financial management. Investment decisions determine how to best allocate capital to maximize returns, while financing decisions determine how to obtain the necessary funds to support these investments and operations. By clearly distinguishing between these two concepts, businesses and investors can make more informed decisions that align with their strategic goals and financial objectives.
Difference Between Investment and Financing
In the world of finance, the terms “investment” and “financing” are often used interchangeably, but they refer to distinct activities with different objectives and implications. Understanding the difference between these two concepts is crucial for effective financial management and strategic decision-making. Let’s explore what sets investment and financing apart.
Investment: Allocating Resources for Future Gains
Purpose: The primary goal of investment is to allocate resources—typically capital—into assets or projects that are expected to generate returns over time. Investments are made with the expectation of future gains, such as income, appreciation, or both.
Key Activities:
- Capital Expenditures: This involves purchasing physical assets like machinery, buildings, or technology to enhance production capacity or efficiency.
- Securities: Investors buy stocks, bonds, or other financial instruments to earn dividends, interest, or capital gains.
- Research and Development (R&D): Companies invest in innovation and new product development to drive future growth.
- Real Estate: Acquiring property for rental income or appreciation is a common investment strategy.
Risk and Return: Investments typically involve varying levels of risk, with the potential for higher returns associated with higher risk. The goal is to maximize returns while managing risk effectively.
Time Horizon: Investments are generally made with a long-term perspective, focusing on future benefits and growth. This long-term view helps investors ride out short-term market volatility and capitalize on compounding returns.
Financing: Raising Capital to Fund Operations
Purpose: Financing involves raising capital to fund the operations, investments, and growth of a business. It focuses on how to obtain the necessary funds to support business activities and investments.
Key Activities:
- Equity Financing: This involves raising capital by issuing shares of stock, effectively selling ownership stakes in the company to investors.
- Debt Financing: Companies borrow funds through loans, bonds, or other debt instruments, which require repayment with interest over time.
- Internal Financing: Using retained earnings or profits generated by the business to fund operations and investments is a common practice.
- Hybrid Financing: Combining elements of both equity and debt, such as issuing convertible bonds or preferred shares, can provide flexible financing options.
Cost and Obligation: Financing decisions involve costs, such as interest payments on debt or dilution of ownership with equity. The choice between debt and equity financing affects the company’s capital structure and financial obligations.
Time Horizon: Financing can be short-term (e.g., working capital loans) or long-term (e.g., issuing bonds or equity). The time horizon depends on the nature of the funding needs and the company’s strategic goals.
The type of the investment
Government Funding
Governments around the world play a crucial role in supporting businesses through various funding mechanisms. These funds are designed to stimulate economic growth, foster innovation, and achieve strategic national objectives. Here, we delve into the different types of government funding available to corporations.
1. Grants
Grants are non-repayable funds provided by the government to support specific projects or activities. They are often awarded to promote research and development, innovation, and public services.
- Research Grants: These grants are aimed at supporting scientific research and technological development. Universities, research institutions, and private companies can apply for these funds to advance their research projects.
- Innovation Grants: Designed to support startups and companies developing new technologies, innovation grants help bring groundbreaking ideas to market.
- Infrastructure Grants: These funds are allocated for the construction and maintenance of public infrastructure such as roads, bridges, and public facilities, ensuring the development of essential services.
2. Subsidies
Subsidies are financial assistance provided to reduce the cost of goods and services, making them more affordable and encouraging production and consumption.
- Agricultural Subsidies: These subsidies support farmers by stabilizing food prices and ensuring food security. They help farmers manage the costs of production and maintain a stable supply of agricultural products.
- Energy Subsidies: Financial aid for renewable energy projects aims to promote sustainable energy sources. These subsidies help reduce the cost of developing and deploying renewable energy technologies.
- Housing Subsidies: Assistance is provided to make housing more affordable for low-income families, ensuring access to safe and stable living conditions.
3. Tax Incentives
Tax incentives are reductions in tax obligations to encourage certain activities or investments. These can take various forms, including tax credits, deductions, and exemptions.
- R&D Tax Credits: These credits reduce the tax burden for companies investing in research and development, encouraging innovation and technological advancement.
- Investment Tax Credits: Incentives for businesses to invest in new equipment or facilities, helping them expand and modernize their operations.
- Employment Tax Credits: Reductions in taxes for companies that create new jobs or hire from specific groups, such as veterans or individuals from disadvantaged backgrounds.
4. Loans and Loan Guarantees
Governments provide loans or guarantee loans to reduce the risk for lenders and make it easier for businesses to access capital.
- Small Business Loans: Low-interest loans are offered to help small businesses start or expand. These loans provide the necessary capital for growth and development.
- Export Financing: Loans and guarantees support companies exporting goods and services, helping them enter and compete in international markets.
- Disaster Recovery Loans: Financial assistance is provided for businesses affected by natural disasters, helping them recover and rebuild.
5. Public-Private Partnerships (PPPs)
PPPs are collaborative agreements between governments and private sector companies to finance, build, and operate projects. These partnerships leverage the strengths of both sectors to deliver public services and infrastructure.
- Infrastructure Projects: Joint ventures are formed to build and maintain roads, bridges, and public transportation systems, ensuring the development of essential infrastructure.
- Healthcare Facilities: Partnerships are established to construct and manage hospitals and clinics, improving access to healthcare services.
- Educational Institutions: Collaborations are developed to build and operate schools and universities, enhancing educational opportunities.
6. Equity Investments
In some cases, governments may take an equity stake in companies, particularly in strategic industries or during economic crises.
- Sovereign Wealth Funds: Government-owned investment funds invest in a variety of assets, including corporate equity, to generate returns for future generations.
- Bailouts: During economic crises, governments may purchase equity in struggling companies to stabilize the economy and prevent widespread financial collapse.
Objectives of Government Funding
- Economic Development: Stimulating economic growth, creating jobs, and enhancing competitiveness are primary goals of government funding. By providing financial support, governments can help businesses expand and thrive.
- Innovation and R&D: Driving technological advancement and maintaining a competitive edge in global markets are key objectives. Government funding supports research and development efforts, fostering innovation.
- Strategic Interests: Securing national security, technological leadership, and energy independence are critical strategic goals. Investments in defense, technology, and energy sectors help achieve these objectives.
- Social and Environmental Goals: Achieving social objectives like affordable housing and environmental sustainability is also a priority. Government funding supports initiatives that improve quality of life and protect the environment.
Government funding supports businesses and achieves broader economic and social goals. Governments can foster innovation, drive economic growth, and address critical societal challenges by providing financial assistance, tax incentives, and strategic investments.
Investment Banks
Investment banks are financial institutions that assist companies in raising capital and provide advisory services for mergers and acquisitions (M&A). They are typically involved in underwriting new debt and equity securities, facilitating the sale of these securities, and helping companies navigate complex financial transactions.
Key Functions of Investment Banks:
- Capital Raising: Investment banks help companies issue new securities, such as stocks and bonds, to raise capital. This includes Initial Public Offerings (IPOs) and secondary offerings.
- Advisory Services: They provide strategic advice on M&A, restructurings, and other financial transactions, including valuation, negotiation, and deal structuring.
- Sales and Trading: These banks facilitate the buying and selling of securities for clients and for their own accounts, providing liquidity to the markets.
- Research: Investment banks conduct in-depth research on industries, companies, and financial instruments, offering valuable insights and recommendations to investors.
Private Equity (PE)
Private equity firms invest in companies that are not publicly traded, often acquiring controlling stakes with the aim of improving their operations and financial performance. These firms typically focus on mature companies that require restructuring or expansion.
Key Characteristics of Private Equity:
- Leveraged Buyouts (LBOs): PE firms often use borrowed funds to acquire companies, aiming to enhance their value through operational improvements.
- Operational Improvements: After acquisition, PE firms work on optimizing business processes, cutting costs, and restructuring management to boost profitability.
- Exit Strategies: PE firms seek to exit their investments profitably through IPOs, sales to other firms, or selling back to the original owners.
- Fund Structure: PE firms raise capital from institutional investors and high-net-worth individuals, pooling this capital into funds used for investments.
Venture Capital (VC)
Venture capital firms provide funding to startups and early-stage companies with high growth potential. They take on significant risk by investing in unproven companies but stand to gain substantial returns if these companies succeed.
Key Characteristics of Venture Capital:
- Stages of Investment: VCs invest in various stages of a startup’s lifecycle, from seed funding to later-stage funding for growth and expansion.
- Portfolio Management: VCs manage a portfolio of investments, spreading risk across multiple startups and providing ongoing support and resources.
- Exit Strategies: Successful exits for VCs include IPOs, acquisitions by larger companies, or secondary sales to other investors.
- Industry Focus: Many VC firms specialize in specific industries, leveraging their expertise and networks to support their portfolio companies.
Corporate Venture Capital (CVC)
Corporate venture capital involves large corporations investing in startups, often to gain strategic advantages such as access to new technologies or markets. CVCs combine financial and strategic goals, seeking both returns and synergies with the parent company’s core business.
Key Characteristics of Corporate Venture Capital:
- Strategic Investments: CVCs invest in startups that align with the parent company’s strategic objectives, such as innovation or market expansion.
- Integration and Synergies: CVCs look for opportunities to integrate the startup’s technology or products with the parent company’s operations, creating mutual benefits.
- Long-Term Perspective: CVCs may have a longer investment horizon compared to traditional VCs, focusing on strategic alignment rather than quick financial returns.
- Collaboration and Support: Startups backed by CVCs often benefit from the parent company’s resources, including expertise, infrastructure, and market access.
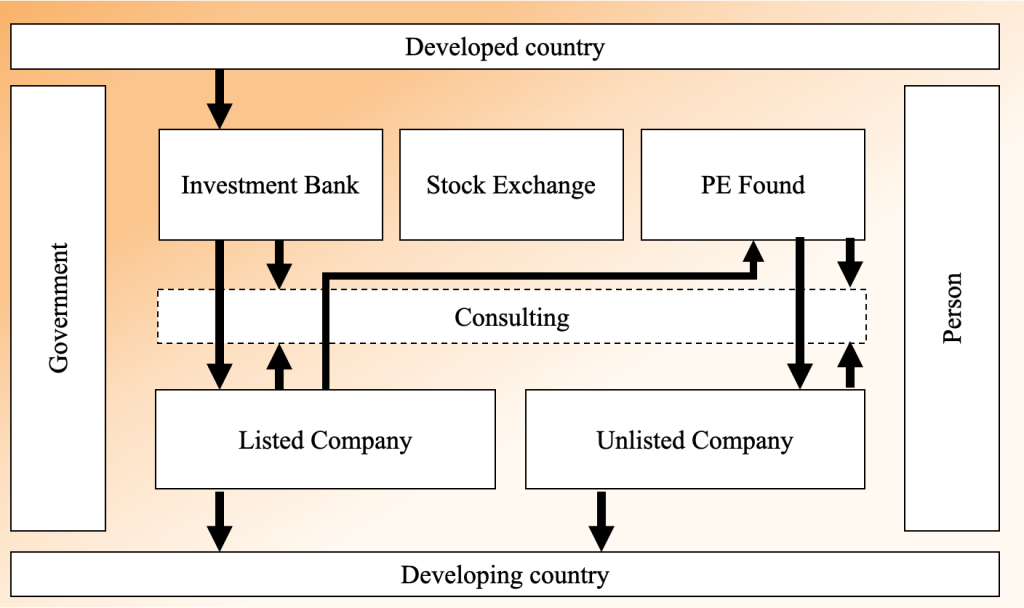
SASAL Support
This is the supply chain of the corporations. SASAL, INC is a strategy corporation; therefore, we can support both sides of the investment and business corporation. In the case of a business corporation, when you would not want to share the capital, SASAL, INC can support it as a strategy consulting firm. In the case of an investment corporation, SASAL, INC can support by searching the details of the market or corporation through business due diligence. SASAL, INC’s support is really flexible; first, please make a contract with the Counselor service. Thank you.