Executive Summary
Expanding into global markets is one of the most powerful ways to scale your business, unlock new revenue streams, and build long-term resilience. However, in 2025’s complex geopolitical and economic environment, success requires a sharp understanding of international trends, supply chain strategy, and value creation at every level of the organization.
General Information
Market Trends
- Protectionism & Trade Tensions
Global trade is under strain due to rising tariffs and policy shifts, particularly in the U.S. and China. Businesses are responding by diversifying markets and localizing operations. - Digital Globalization
Cross-border e-commerce, SaaS, and cloud-based services are booming. Businesses no longer need physical presence to expand globally, making international reach more accessible. - Sustainability Demands
Consumers and regulators alike are pushing for environmentally responsible supply chains. Companies that adopt green practices are gaining both reputational and financial advantages. - Local Talent & Remote Teams
With remote work becoming the norm, global hiring is a new growth lever. Hiring local experts in key markets improves market penetration and customer insights. - Resilient Supply Chains
Flexibility is now a top priority. Global businesses are investing in digital logistics, multi-region sourcing, and predictive analytics to reduce vulnerability.

Stock Performance
Here’s how different markets and sectors are faring in Q2 of 2025:
| Region | Market Outlook | Key Movers |
|---|---|---|
| U.S. | Slowing growth, with recession fears (1.8% GDP growth forecast). | Consumer goods, logistics, and big tech underperforming. |
| Europe | Relative stability, driven by green tech and AI investment. | Renewable energy, enterprise SaaS showing strength. |
| Asia | Mixed results. China stabilizing with rate cuts; India and ASEAN growing fast. | Defense, fintech, and infrastructure strong performers. |
| Emerging Markets | Volatile but high potential for long-term investors. | Local e-commerce, telecoms expanding rapidly. |
Opportunity: Global companies that localize products and services are outperforming their domestic-only competitors.
Risk: Overexposure to any one market or region can significantly affect valuation during political or economic shocks.
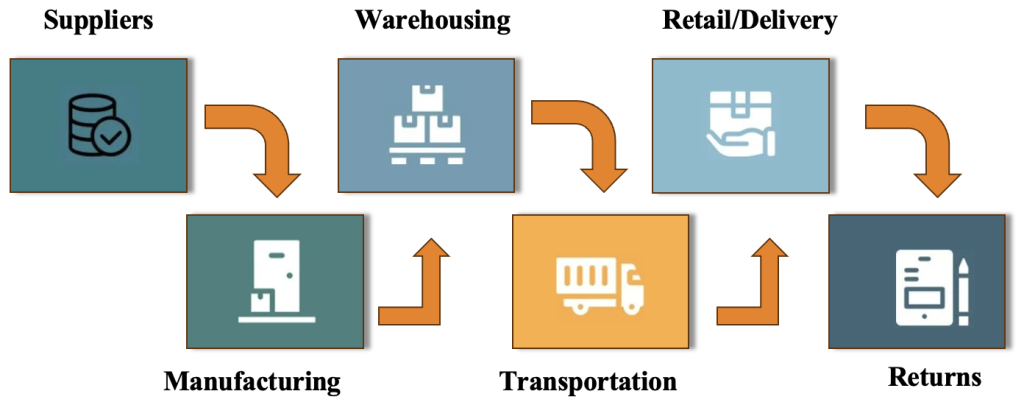
Business Model (Value Chain)
- Inbound Logistics – Source materials globally while navigating customs and regulations.
- Operations – Manufacture or assemble products efficiently across international locations.
- Outbound Logistics – Distribute products through global shipping and logistics networks.
- Marketing & Sales – Adapt messaging and pricing to local cultures and markets.
- Service – Provide multilingual, regionally-supported customer service.

Business Environment (Supply Chain)
- Suppliers – Work with international vendors to secure quality materials.
- Manufacturing – Choose strategic global sites to reduce costs and improve speed.
- Warehousing – Use international hubs to store and manage inventory closer to demand.
- Transportation – Ship products worldwide via efficient, multimodal routes.
- Retail/Delivery – Sell through global e-commerce and deliver locally.
- Returns – Set up systems to handle cross-border product returns smoothly.
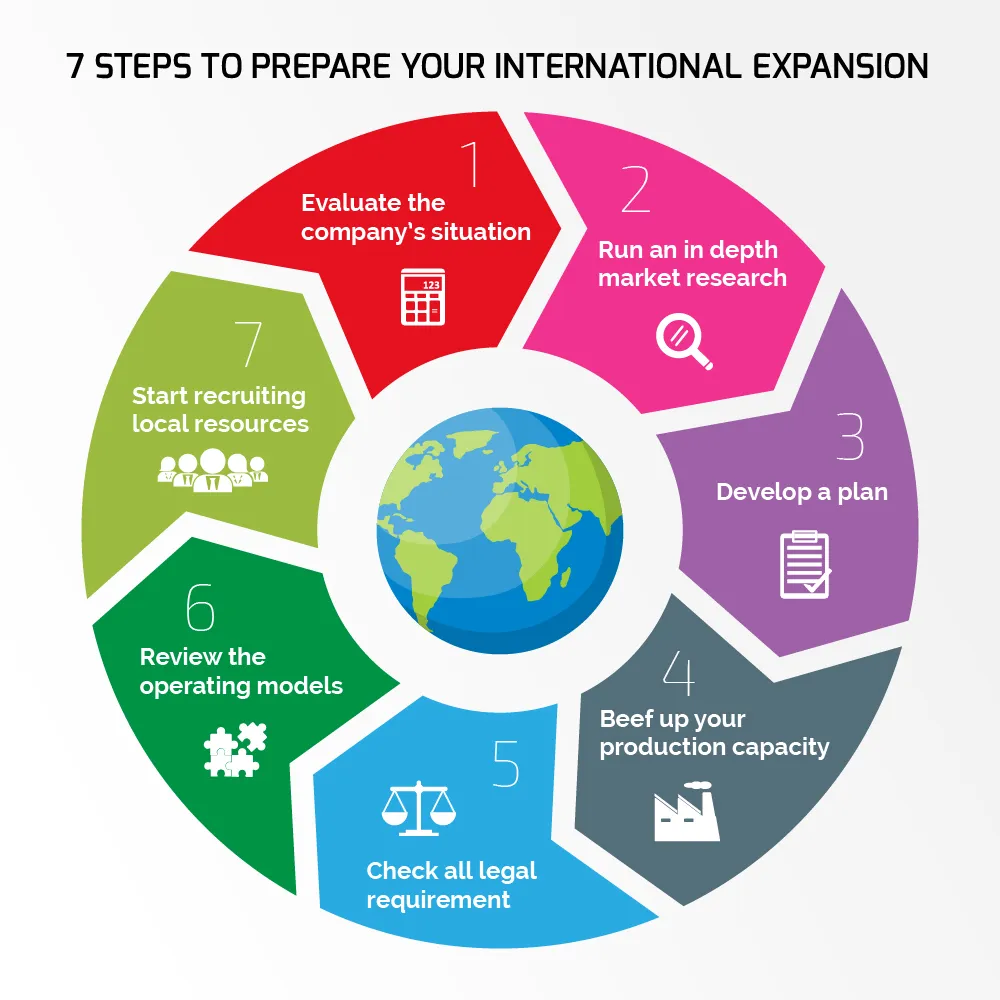
Introducing Steps
- Market Research – Identify target countries, demand, competition, and legal environment.
- Product Readiness – Adapt products for cultural fit, language, legal standards (e.g., packaging, labeling).
- Register Your Business – Set up legal business entities or partners in the new country.
- Build Local Partnerships – Find distributors, agents, or local reps to bridge entry barriers.
- Compliance & Regulations – Understand and follow import/export laws, taxes, tariffs, and trade rules.
- Set Up Payments – Enable international transactions (currencies, taxes, payment platforms).
- Start Small – Test with a pilot launch or through online marketplaces (Amazon, Etsy, Alibaba).
- Customer Support Basics – Offer basic multilingual support and return options.
Advanced Information
Advanced Steps
- Establish Local Offices – Set up regional headquarters or satellite branches for deeper market integration.
- Global Branding Strategy – Develop a unified brand with localized messaging and design.
- Supply Chain Diversification – Use multiple suppliers and logistics partners to manage risk and flexibility.
- Hiring International Teams – Recruit and manage staff in target markets with cultural alignment.
- Global Marketing Campaigns – Run coordinated, multilingual campaigns across platforms and countries.
- Technology Integration – Implement global ERP, CRM, and cloud-based collaboration tools.
- Optimize Tax & Legal Structures – Use international tax planning, IP protection, and local legal advisors.
- Sustainability & Ethics – Ensure ethical sourcing, fair labor, and sustainability to meet global standards.
- M&A or Joint Ventures – Acquire or partner with foreign businesses to accelerate market presence.
SASAL Can Support You
Insourcing
If you’re ready to make global expansion a core part of your business strategy, SASAL is here to guide you every step of the way. With our CSO Sharing Service, you’ll receive expert, personalized support to navigate international markets and drive sustainable growth through strategic, cross-border execution.
Outsourcing
If you’re ready to do business globally but lack the resources or expertise, SASAL can manage the entire process for you. From identifying the right markets to handling local partnerships and integrating into new regions, we take care of everything so you can focus on growth and enjoy the results.
Practice
| Goal | Key Term | Strategy to Achieve |
|---|---|---|
| Expand into 3 new markets | Market Penetration | Conduct market analysis and establish local partnerships. |
| Increase global sales by 25% | Revenue Growth | Enhance digital marketing and optimize supply chains. |
| Achieve 15% cost reduction | Operational Efficiency | Implement automation and negotiate better supplier contracts. |