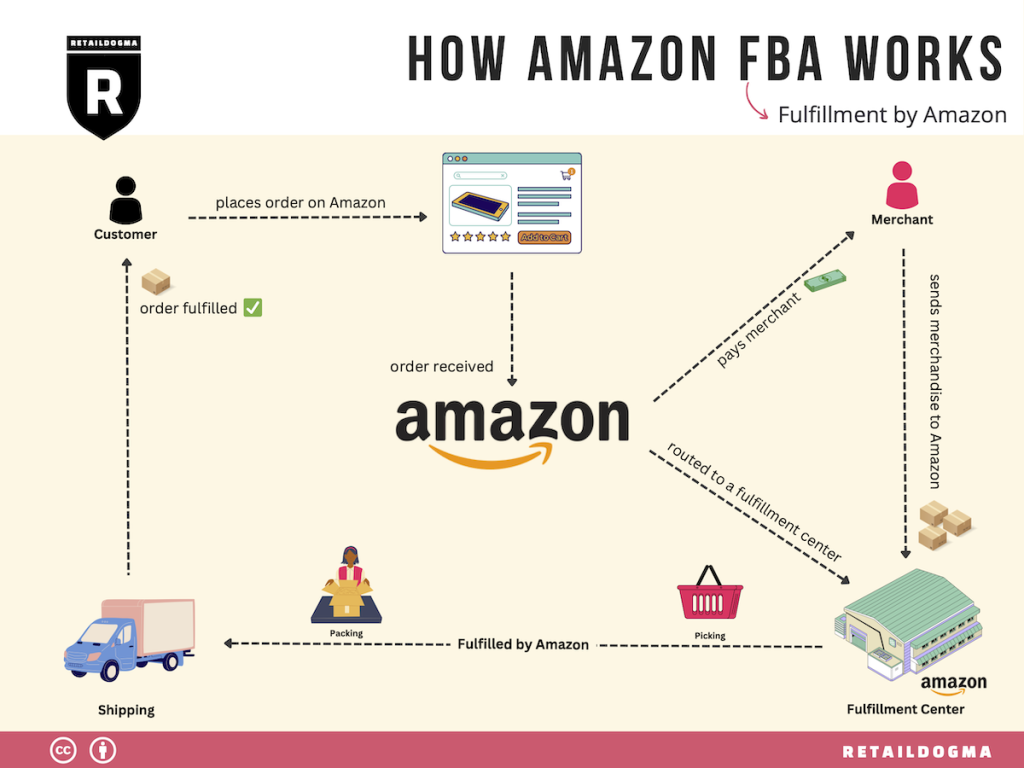
Things you need to consider
- Regulatory Compliance:
- Export Control Regulations: Understand export control laws, such as the U.S. Export Administration Regulations (EAR) and International Traffic in Arms Regulations (ITAR), which govern the export of sensitive technologies and defense-related items.
- Import Quotas: Be aware of import quotas that limit the quantity of certain goods that can be imported into a country during a specific period.
- Harmonized System (HS) Codes: Use the correct HS codes for your products to ensure accurate classification and avoid delays or penalties.
- Transportation Modes:
- Charter Services: For large or specialized shipments, consider chartering a vessel or aircraft. This can provide flexibility and control over the shipping schedule.
- Cold Chain Logistics: For perishable goods, implement cold chain logistics to maintain the required temperature throughout the transportation process.
- Last-Mile Delivery: Plan for efficient last-mile delivery, which is the final step of the shipping process from a distribution center to the end customer.
- Cost Management:
- Freight Rate Negotiation: Regularly negotiate freight rates with carriers to secure the best possible terms.
- Duty Drawback Programs: Explore duty drawback programs that allow for the refund of duties paid on imported goods that are subsequently exported.
- Cost Allocation: Implement cost allocation methods to accurately distribute transportation costs across different departments or products.
- Vendor Management:
- Supplier Risk Assessment: Conduct thorough risk assessments of suppliers to identify potential vulnerabilities and mitigate risks.
- Supplier Development Programs: Invest in supplier development programs to improve the capabilities and performance of your suppliers.
- Collaborative Planning: Engage in collaborative planning with suppliers to align production schedules and inventory levels.
- Cultural and Ethical Considerations:
- Language Barriers: Address language barriers by employing multilingual staff or using translation services to facilitate communication.
- Local Holidays and Customs: Be mindful of local holidays and customs that may affect business operations and shipping schedules.
- Ethical Sourcing: Ensure that your sourcing practices are ethical, including fair labor practices and environmentally sustainable methods.
- Quality Control:
- Statistical Process Control (SPC): Use SPC techniques to monitor and control production processes, ensuring consistent quality.
- Corrective and Preventive Actions (CAPA): Implement CAPA processes to address quality issues and prevent recurrence.
- Supplier Quality Agreements: Establish quality agreements with suppliers that outline specific quality requirements and expectations.
- Logistics and Documentation:
- Advanced Shipping Notices (ASN): Use ASNs to provide detailed information about upcoming shipments, improving visibility and planning.
- Document Management Systems: Implement document management systems to organize and store all shipping-related documents electronically.
- Customs Valuation: Ensure accurate customs valuation of goods to avoid disputes and penalties.
- Risk Management:
- Supply Chain Mapping: Map out your entire supply chain to identify potential risks and dependencies.
- Scenario Planning: Conduct scenario planning exercises to prepare for various risk scenarios and develop appropriate responses.
- Supplier Contingency Plans: Work with suppliers to develop contingency plans for potential disruptions.
SASAL, INC recommendation
SASAL, INC. recommends those steps because we can start with a small budget and lots, which makes it easy for customers to buy. If we could sell the product to the client directly, we would be able to try B2B selling by using our past case of B2C selling; we would be able to sell to a wider market by using Amazon because if you are a beginner at each platform, you need to catch up while selling the small platform.
Clients and SASAL need to improve the product more while selling, so by using SASAL, INC’s current selling platform, and you can pass the test selling with a saving fee.
Surely, you have already tried to sell the product on Amazon and Alibaba, and there is a budget and lots; in that case, it’s no problem to start from those platforms.
For that service, you need to contact the SASAL counselor service. Please feel free to contact us. Thank you.
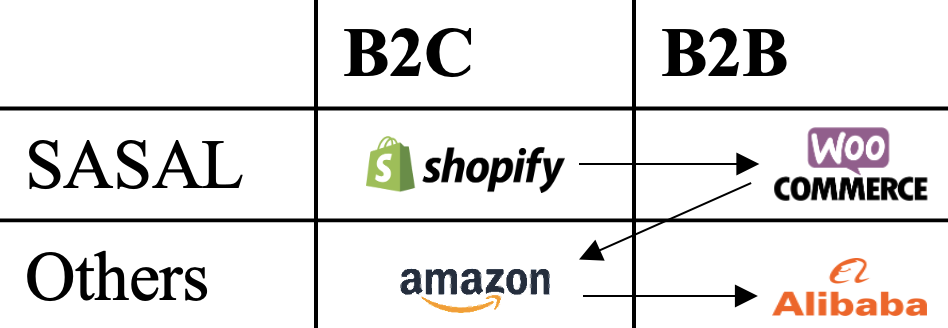
| Shopify | Woo Commerce | Amazon | Alibaba | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Difficulty | Easy | Easy | Middle | Difficult |
| Budget | Low | Low | High | High |
| Operating Margin | High | High | Low | Low |
| Lot | Small | Middle | Small | High |
| Advertisement Fee | No SASAL prepares | No SASAL prepares | High Client Budget | Small Client Budget |
| Insourcing Difficulty | Easy | High | Middle | Middle |
* When the client would like to insource the environment, SASAL recommends from Amazon environment.